Tests in the OpenMetadata UI
Here you can see all the supported tests definitions and how to configure them in the UI.
A Test Definition is a generic definition of a test. This Test Definition then gets specified in a Test Case. This Test Case is where the parameter(s) of a Test Definition are specified.
In this section, you will learn what tests we currently support and how to configure them in the OpenMetadata UI.
Table Tests
Tests applied on top of a Table. Here is the list of all table tests:
- Table Row Count to Equal
- Table Row Count to be Between
- Table Column Count to Equal
- Table Column Count to be Between
- Table Column Name to Exist
- Table Column to Match Set
- Table Custom SQL Test
- Table Row Inserted Count To Be Between
- Compare 2 Tables for Differences
- Table Data to Be Fresh [Collate]
Table Row Count to Equal
Validate that the total number of rows in a table exactly matches an expected value.**
When to Use
- To monitor tables where row count is expected to remain fixed (e.g., dimension tables).
- To catch over- or under-loading issues after ETL processes.
- To verify baseline data volumes for test/staging/prod comparisons.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Expected Value | The exact number of rows the table should contain. |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Actual row count = expected value | ✅ Success |
| Actual row count ≠ expected value | ❌ Failed |
Table Row Count to be Between
Ensure that the total number of rows in the table falls within an expected range.
When to Use
- To monitor for abnormal growth or shrinkage in table size.
- To catch failed inserts, unintended truncations, or unexpected data surges.
- To set alerts based on historical data volume expectations.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Min Value | Minimum expected number of rows (minValue) |
| Max Value | Maximum allowed number of rows (maxValue) |
- At least one of these values is required to run the test.
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Row count is between minValue and maxValue | ✅ Success |
| Row count is outside the defined range | ❌ Failed |
Table Column Count to Equal
Validate that the table contains exactly the expected number of columns.
When to Use
- To detect unapproved schema changes (e.g., columns being added or dropped).
- To enforce data contracts between teams or systems.
- To ensure structural consistency across environments.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Expected Count | Exact number of columns the table must have. |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Actual column count = expected count | ✅ Success |
| Actual column count ≠ expected count | ❌ Failed |
Table Column Count to be Between
Validate that the number of columns in a table falls within a defined range.
When to Use
- To detect schema drift or changes in table structure.
- To ensure a table has a predictable number of columns across environments (e.g., staging vs. production).
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Min Columns | Minimum number of expected columns (minColValue) |
| Max Columns | Maximum number of allowed columns (maxColValue) |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Actual column count is within the defined range | ✅ Success |
| Actual column count is outside the defined range | ❌ Failed |
Table Column Name to Exist
Ensure that a specific column is present in the table schema.
When to Use
- To validate that required schema fields exist (e.g.,
order_id,customer_id). - To monitor schema changes that might break downstream processes.
- To enforce critical column presence in governed datasets.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Column Name | Name of the column that must exist in the table. |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
columnName exists in the table schema | ✅ Success |
columnName is missing from the table | ❌ Failed |
Table Column to Match Set
Validate that a table’s column names match a predefined set — with or without order sensitivity.
When to Use
- To ensure schema alignment across different environments or pipeline stages.
- To detect unexpected column additions, deletions, or reordering.
- To enforce table contracts where the exact structure is critical.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Column Names | Comma-separated list of expected column names (e.g., col1, col2, col3) |
| Ordered | Boolean flag (true or false) — whether the order of columns must match. |
Test Logic
| Ordered | Condition | Status |
|---|---|---|
false | All expected column names exist (any order) | ✅ Success |
true | Column names match and appear in the exact order | ✅ Success |
false | Some columns are missing or extra | ❌ Failed |
true | Columns are present but order is incorrect | ❌ Failed |
Table Custom SQL Test
Use this test to define your own validation logic using a custom SQL expression.
When to Use
- To implement logic beyond predefined test definitions.
- To detect outliers, nulls, duplicates, or business-specific data anomalies.
- When you need full flexibility using SQL syntax.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Expression | The SQL query used to evaluate the test. |
| Strategy | Defines how to interpret the result. Options: ROWS (default) or COUNT. |
| Threshold | The maximum allowed rows or count before marking the test as failed. Default is 0. |
Test Logic
| Strategy | Condition | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ROWS | Number of returned rows ≤ threshold | ✅ Success |
| ROWS | Number of returned rows > threshold | ❌ Failed |
| COUNT | Count result ≤ threshold | ✅ Success |
| COUNT | Count result > threshold | ❌ Failed |
Table Row Inserted Count To Be Between
Check that the number of rows inserted during a defined time window falls within an expected range.**
When to Use
- To detect whether recent data ingestion volumes are within acceptable limits.
- To monitor time-partitioned tables for daily/hourly/monthly data drops or spikes.
- To validate pipeline freshness and completeness over time.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Min Row Count | Minimum number of inserted rows expected in the given range. |
| Max Row Count | Maximum number of inserted rows allowed in the given range. |
| Column Name | Timestamp column used to filter the inserted rows. |
| Range Type | Time granularity: HOUR, DAY, MONTH, or YEAR. |
| Range Interval | Number of units (e.g., last 1 DAY, 2 HOURS, etc.). |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Row count within min and max for the interval | ✅ Success |
| Row count outside of the expected range | ❌ Failed |
The Table Row Inserted Count To Be Between cannot be executed against tables that have configured a partition in OpenMetadata. The logic of the test performed will be similar to executing a Table Row Count to be Between test against a table with a partition configured.
Compare 2 Tables for Differences
Use this test to verify data consistency between two tables, even across different platforms or services.
When to Use
- After data replication or migration (e.g., Snowflake → Redshift).
- To validate data integrity between source and target systems.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Key Columns | Columns used as the row-matching key. Defaults to the table's primary key if not specified. |
| Columns to Compare | Subset of columns used for comparison. If not provided, all columns will be compared. |
| Second Table | Fully qualified name of the second table (e.g., redshift_dbt.dev.dbt_jaffle.boolean_test). |
| Threshold | Maximum number of mismatched rows allowed. Default is 0 (strict equality). |
| Filter Condition | (Optional) A WHERE clause (e.g., id != 999) to limit rows involved in the comparison. |
| Case-Sensitive Columns | Set to true if column name case must match exactly (default is false). |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Number of differing rows ≤ threshold | ✅ Success |
| Number of differing rows > threshold | ❌ Failed |
🌐 Supported Data Sources
- Snowflake
- BigQuery
- Athena
- Redshift
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MSSQL
- Oracle
- Trino
- SAP Hana
Table Data to Be Fresh [Collate]
Ensure that table data is being updated frequently enough to be considered fresh.
When to Use
- To monitor data pipelines for staleness or lag.
- To detect delays in scheduled batch updates.
- To ensure compliance with SLAs for near real-time data delivery.
Test Summary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Column | The datetime column used to determine the last update. |
| Time Since Update | Time threshold (in seconds) — maximum age of the most recent data entry. |
Test Logic
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Last update time ≤ timeSinceUpdate | ✅ Success |
Last update time > timeSinceUpdate | ❌ Failed |
Column Tests
Tests applied on top of Column metrics. Here is the list of all column tests:
- Column Values to Be Unique
- Column Values to Be Not Null
- Column Values to Match Regex
- Column Values to not Match Regex
- Column Values to Be in Set
- Column Values to Be Not In Set
- Column Values to Be Between
- Column Values Missing Count to Be Equal
- Column Values Lengths to Be Between
- Column Value Max to Be Between
- Column Value Min to Be Between
- Column Value Mean to Be Between
- Column Value Median to Be Between
- Column Values Sum to Be Between
- Column Values Standard Deviation to Be Between
- Column Values To Be At Expected Location
Column Values to Be Unique
Ensures each value in a column appears only once.
Dimension
Uniqueness
When to Use
- Primary keys or natural identifiers
- Fields like email, username, or ID
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| All values are unique | ✅ |
| Any duplicate value found | ❌ |
Column Values to Be Not Null
Ensures there are no NULL entries in the column.
Dimension
Completeness
When to Use
- Mandatory fields such as
email,amount,created_at - Required keys or business-critical columns
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| No NULLs present | ✅ |
| Any NULL value present | ❌ |
Column Values to Match Regex
This test allows us to specify how many values in a column we expect that will match a certain regex expression. Please note that for certain databases we will fall back to SQL LIKE expression. The databases supporting regex pattern as of 0.13.2 are:
- redshift
- postgres
- oracle
- mysql
- mariaDB
- sqlite
- clickhouse
- snowflake
Ensures all values match a specified regular expression pattern.
Dimension
Validity
When to Use
- Emails, zip codes, IDs, structured formats
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| All values match regex | ✅ |
| Any value does not match | ❌ |
Column Values to not Match Regex
This test allows us to specify values in a column we expect that will not match a certain regex expression. If the test find values matching the forbiddenRegex the test will fail. Please note that for certain databases we will fall back to SQL LIKE expression. The databases supporting regex pattern as of 0.13.2 are:
- redshift
- postgres
- oracle
- mysql
- mariaDB
- sqlite
- clickhouse
- snowflake
The other databases will fall back to the LIKE expression
Ensures values do not match a restricted regex pattern.
Dimension
Validity
When to Use
- Prevent forbidden values, test strings, or patterns
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| No value matches forbidden pattern | ✅ |
| Any value matches the pattern | ❌ |
Column Values to Be in Set
Ensures values are within a predefined whitelist.
Dimension
Validity
When to Use
- Enum values:
status,currency,country_code
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
All values in set (if matchEnum = true) | ✅ |
Any value not in set (if matchEnum = true) | ❌ |
Any value from set exists (if matchEnum = false) | ✅ |
No values from set found (if matchEnum = false) | ❌ |
Column Values to Be Not In Set
Ensures values are not in a specified blacklist.
Dimension
Validity
When to Use
- Block invalid values like
"NA","Unknown",-1
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| No values from forbidden set | ✅ |
| Any value from forbidden set found | ❌ |
Column Values to Be Between
Validates numeric values of a column are within a given range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Username length, field input length validation
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Length within [min, max] | ✅ |
| Length < min or > max | ❌ |
Column Values Missing Count to Be Equal
Ensures total missing values (NULL + defined "missing" strings) match a target count.
Dimension
Completeness
When to Use
- Auditing known missing values
- Accounting for
"NA","N/A","null"
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Missing count = expected value | ✅ |
| Missing count ≠ expected value | ❌ |
Column Values Lengths to Be Between
Ensures that the length of each string value in the column is within a defined character range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- To validate field length constraints like
name,address, ordescription - To catch too-short or too-long values that may break UI or downstream logic
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
All values have length within [min, max] | ✅ |
| Any value length < min or > max | ❌ |
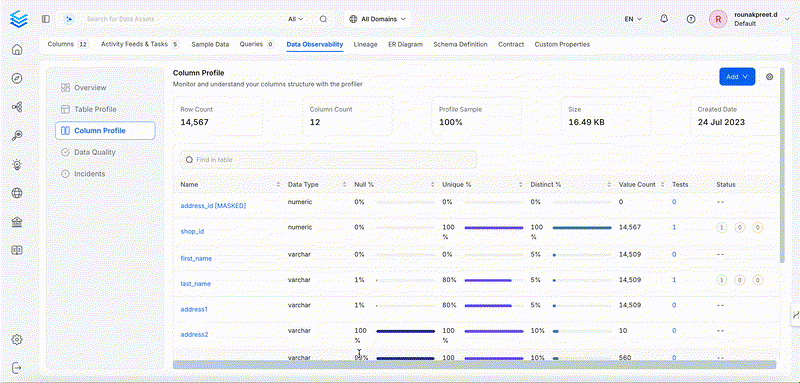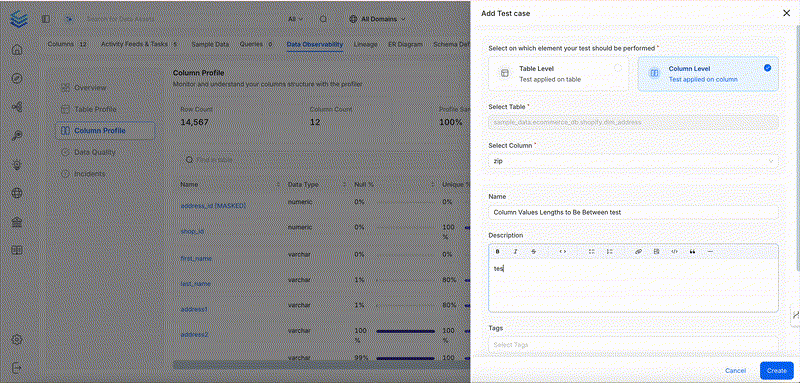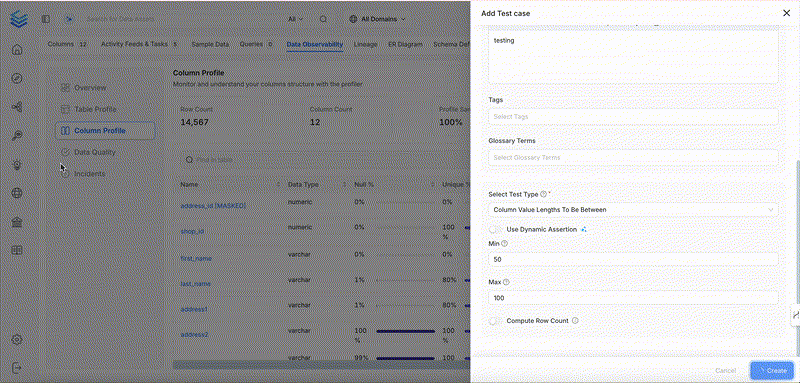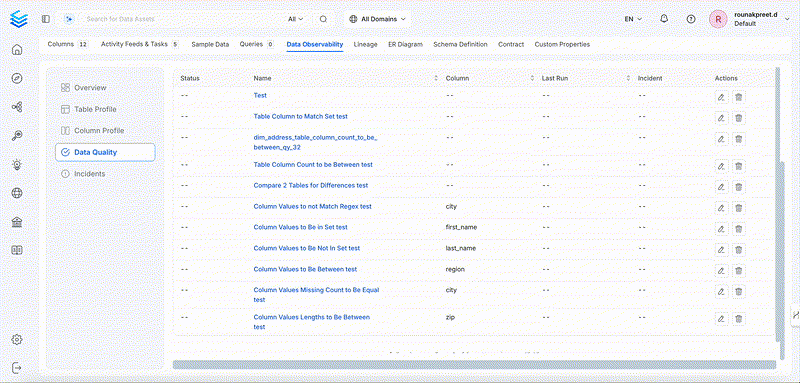
Column Value Max to Be Between
Validates the maximum value of a column lies within a range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Cap validation for
score,amount,age
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Max value in range [min, max] | ✅ |
| Max < min or Max > max | ❌ |
Column Value Min to Be Between
Validates the minimum value of a column lies within a range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Threshold validation for
discount,price, etc.
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Min value in range [min, max] | ✅ |
| Min < min or Min > max | ❌ |
Column Value Mean to Be Between
Validates that the mean (average) value is in the expected range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Check dataset drift or pipeline behavior
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Mean value in [min, max] | ✅ |
| Mean < min or Mean > max | ❌ |
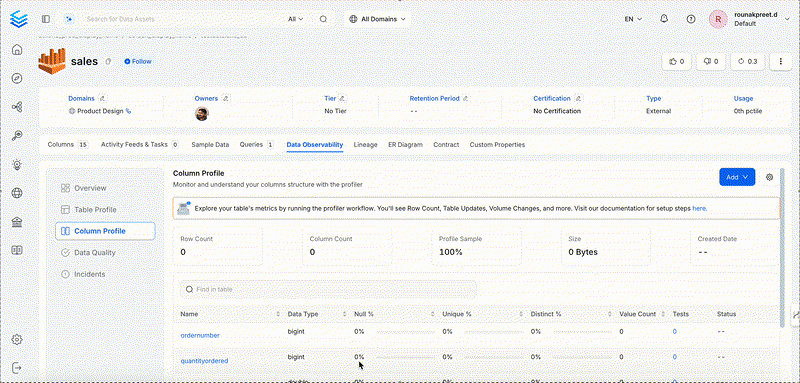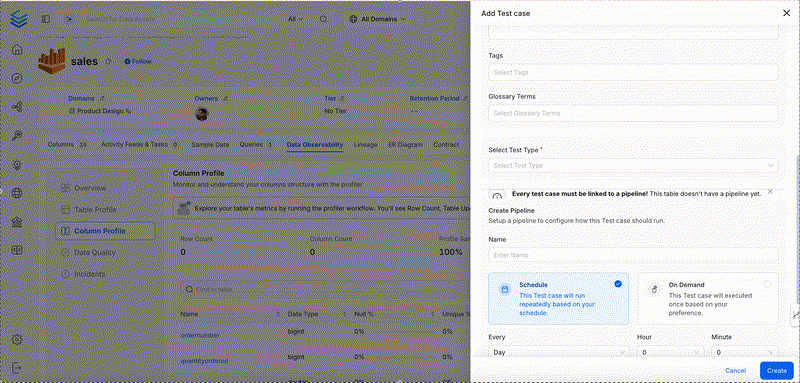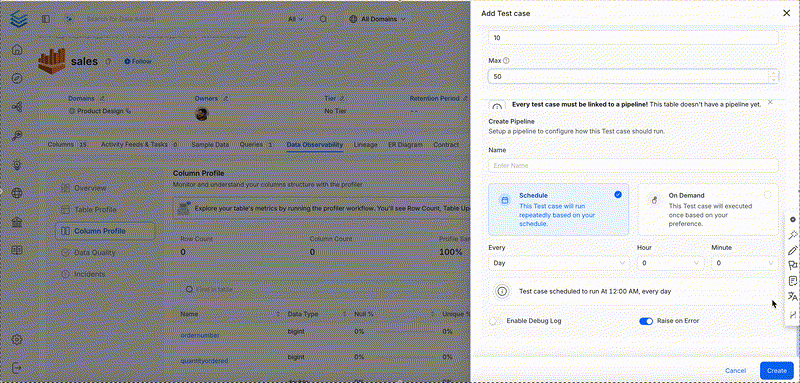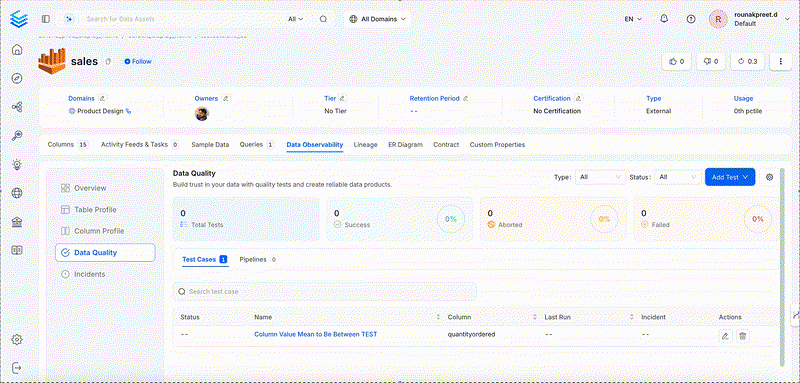
Column Value Median to Be Between
Validates the median value is in the expected range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Median income, score, latency checks
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Median in range [min, max] | ✅ |
| Median < min or Median > max | ❌ |
Column Values Sum to Be Between
Validates the total sum of values in a column is within a defined range.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Revenue, units sold, total scores, etc.
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Sum in range [min, max] | ✅ |
| Sum < min or Sum > max | ❌ |
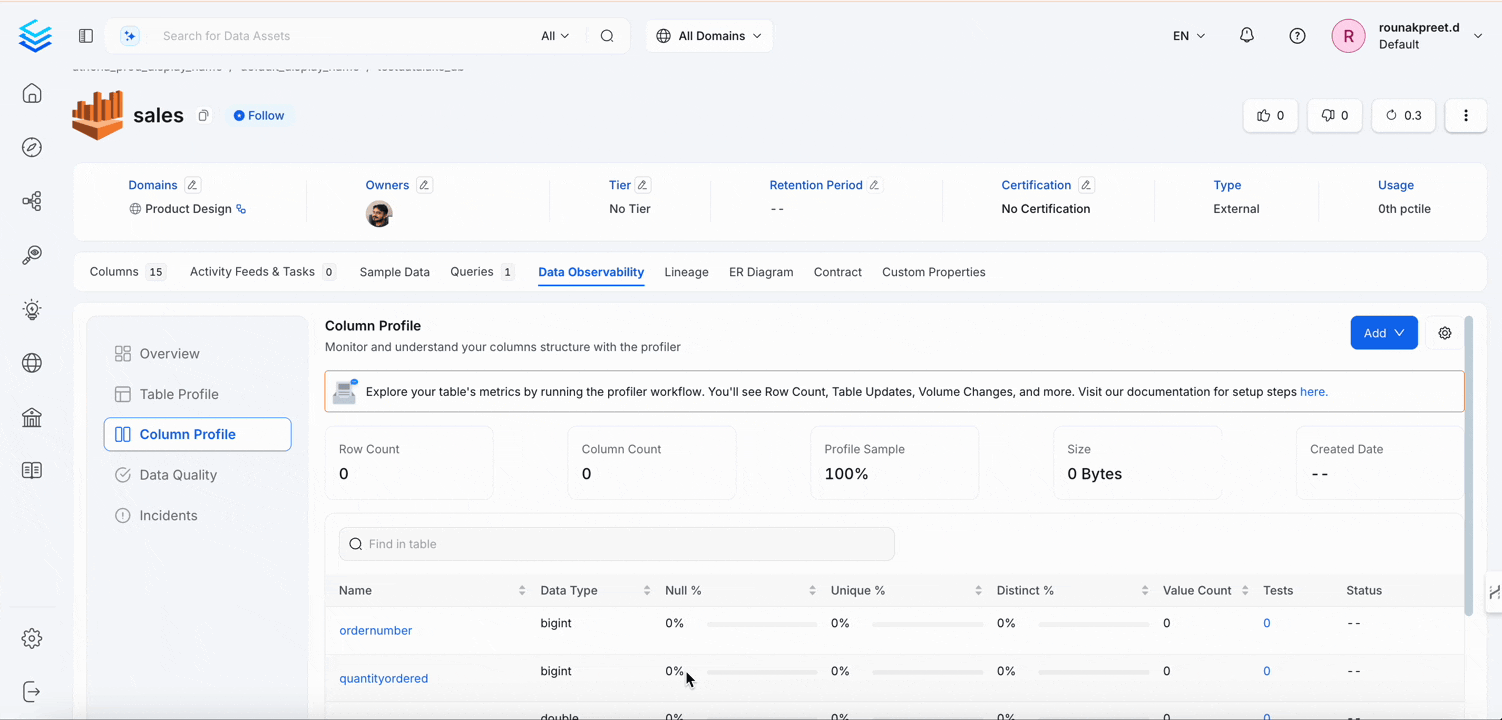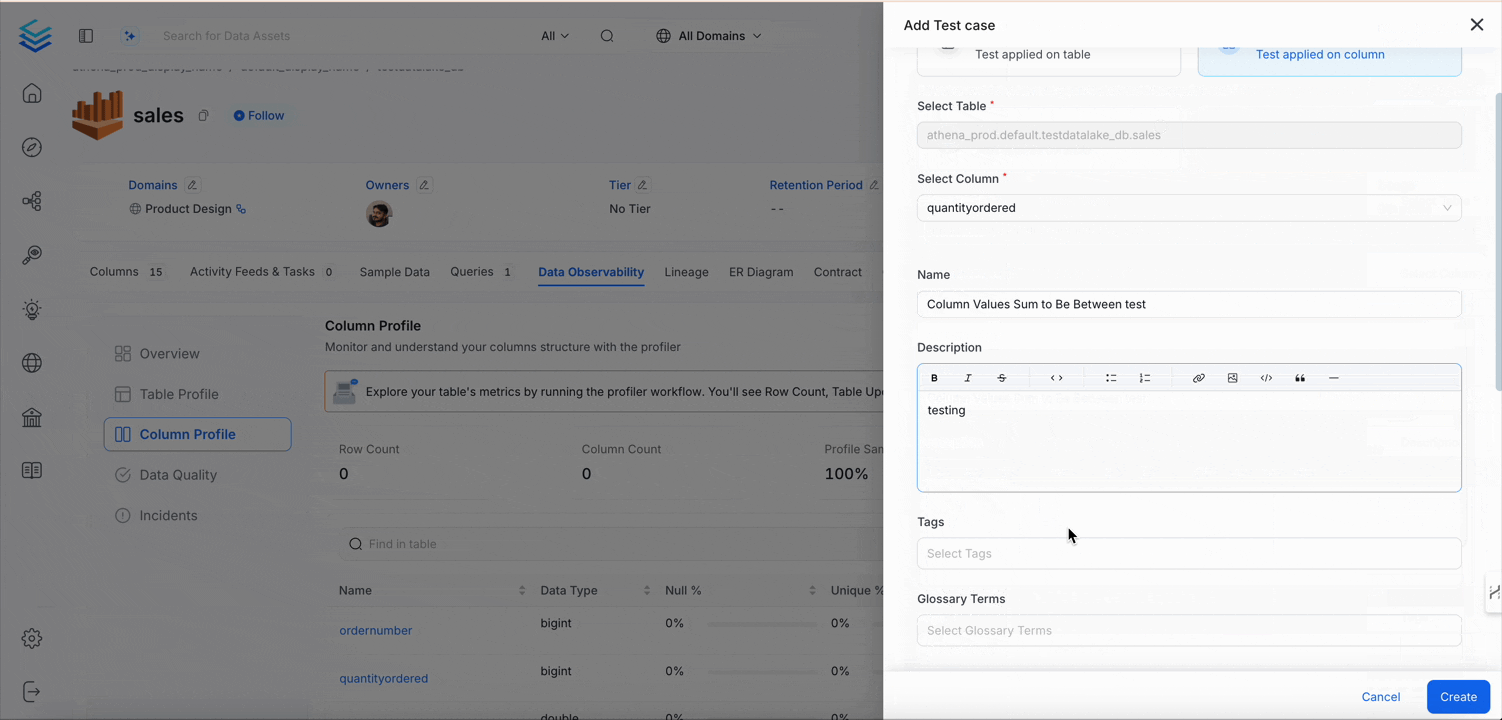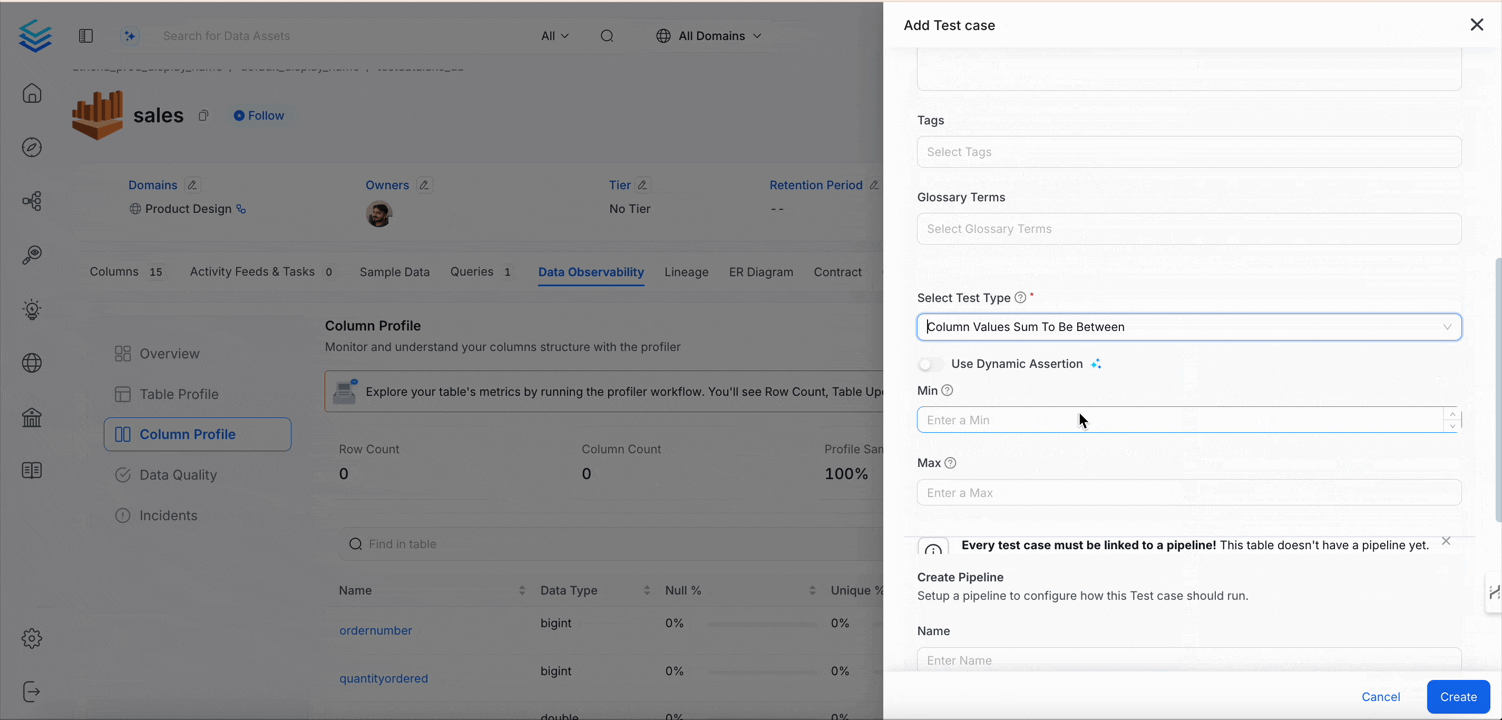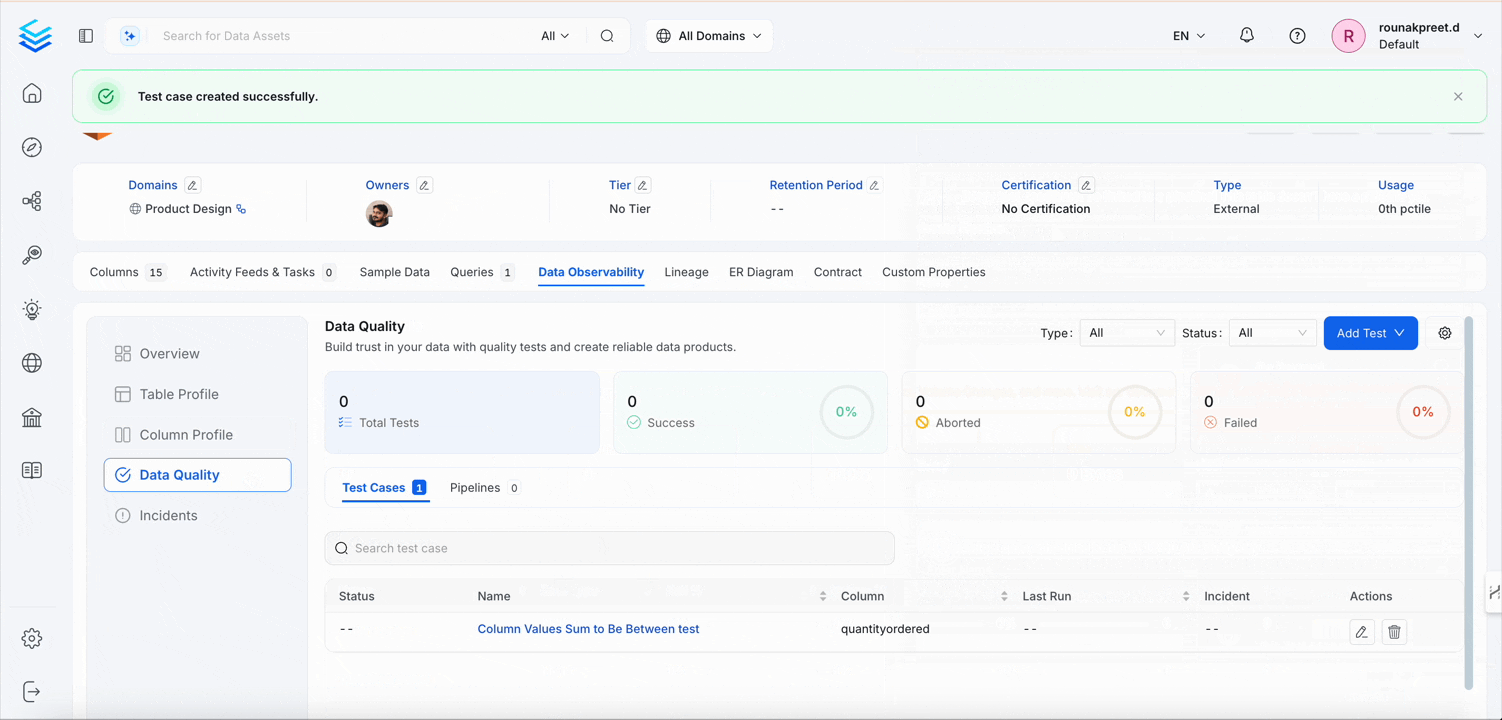
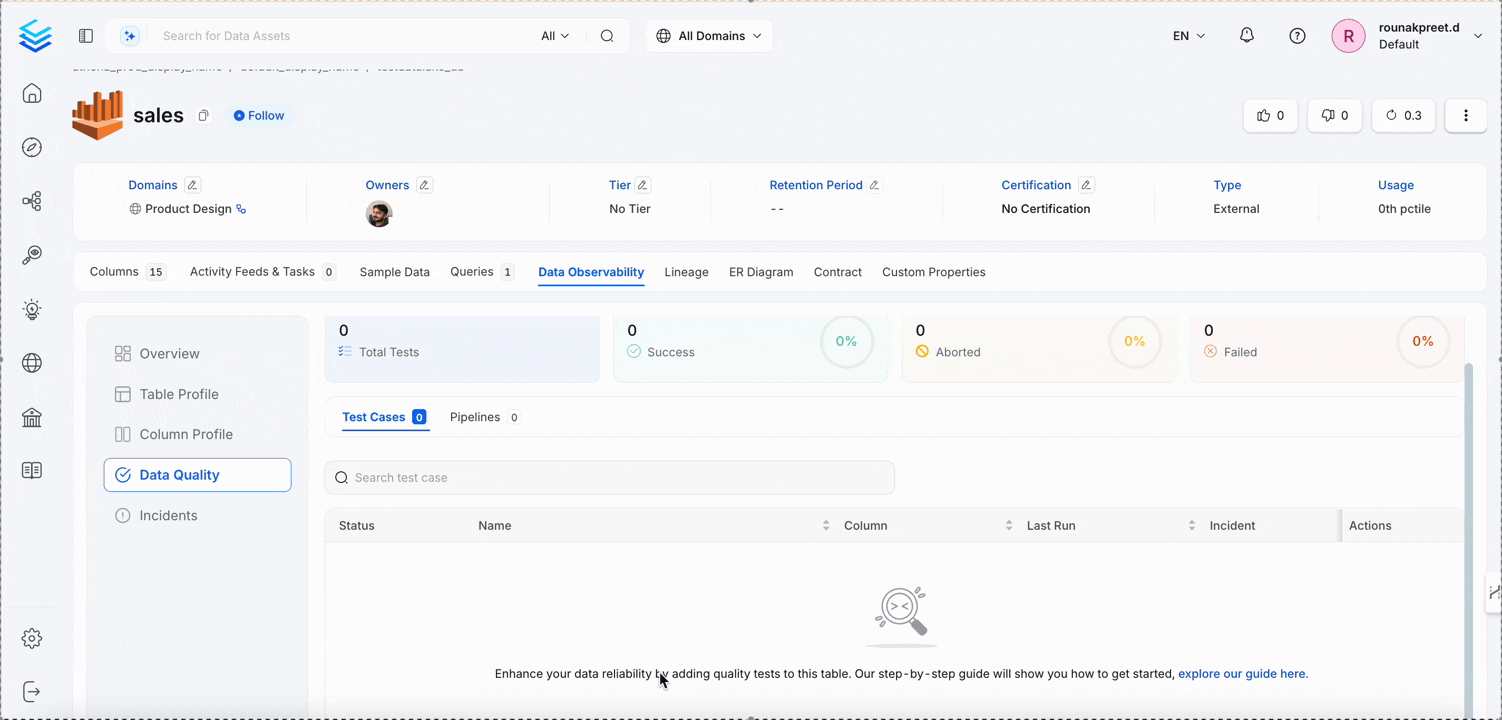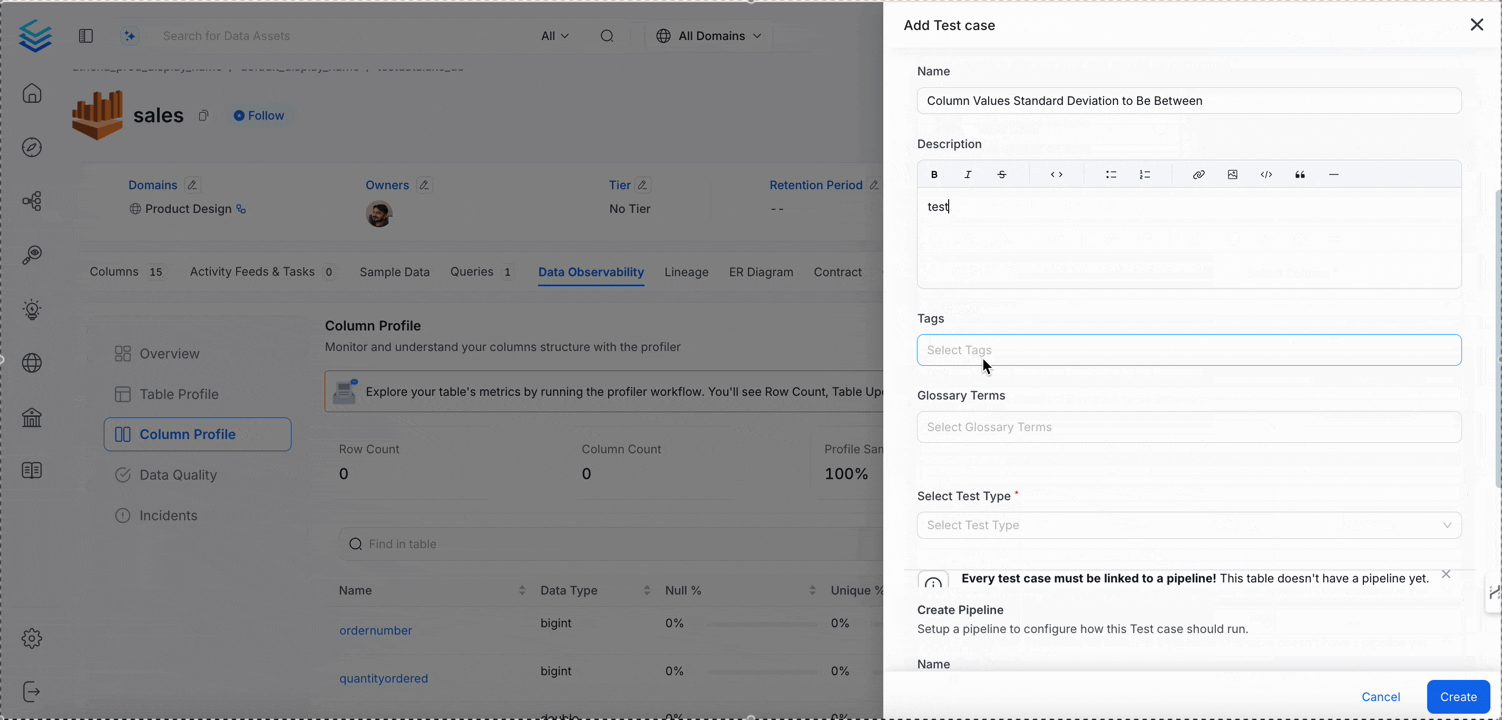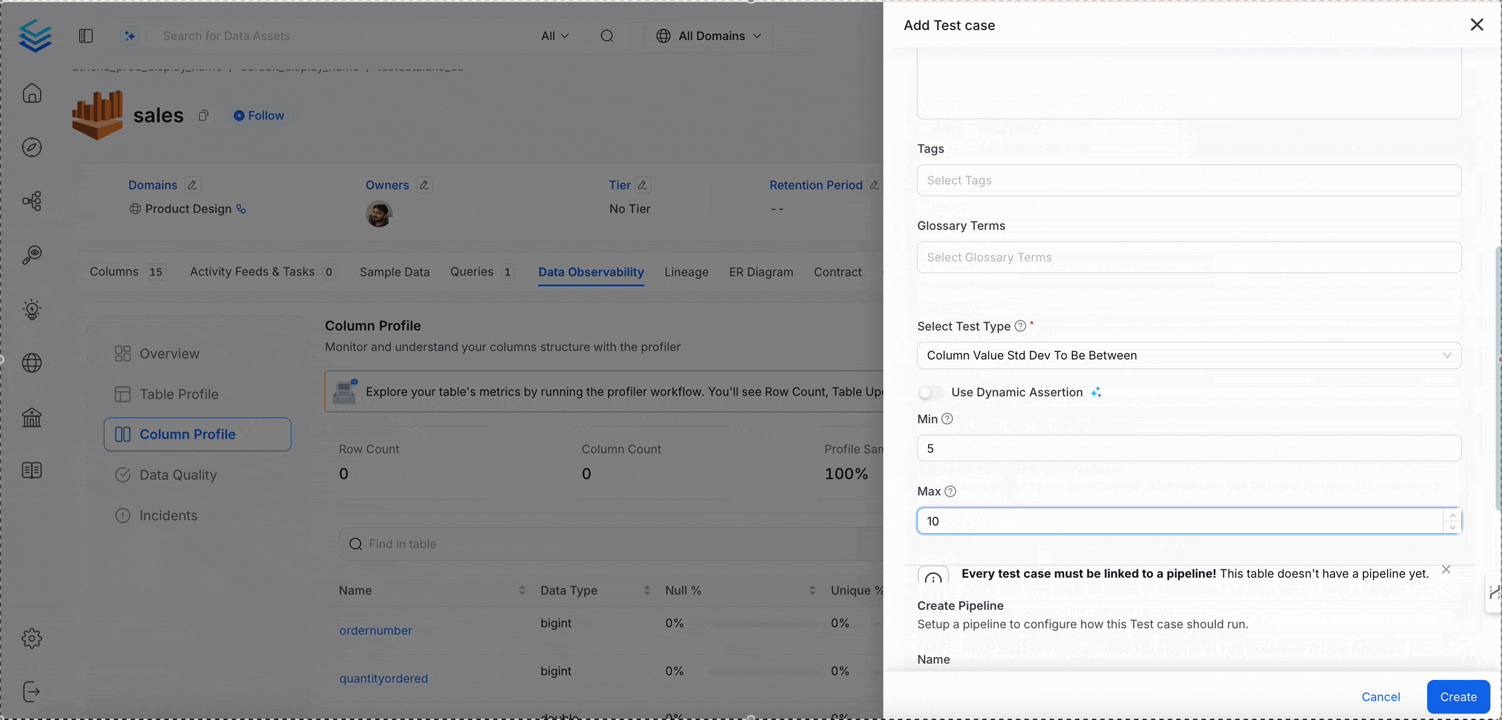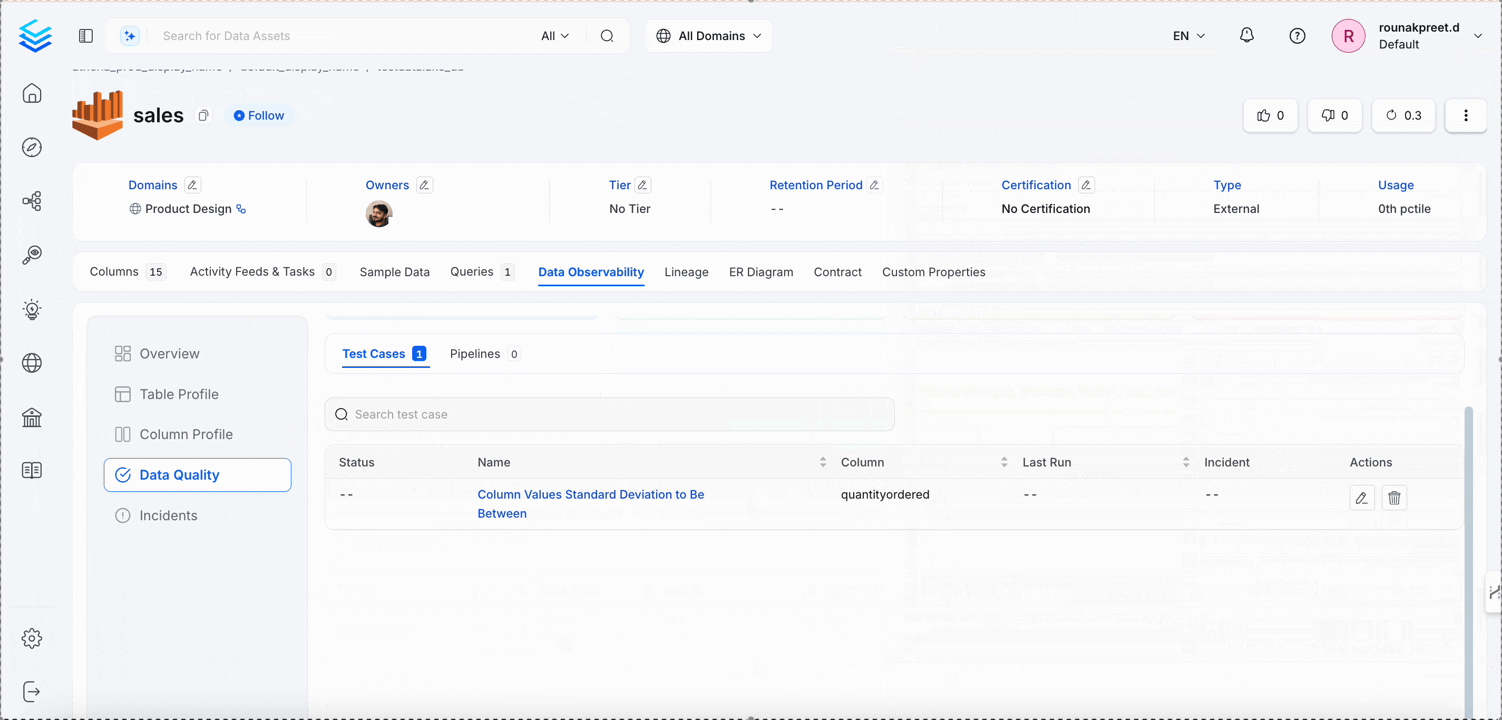
Column Values Standard Deviation to Be Between
Validates the standard deviation (spread) of values is acceptable.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Monitoring variance in numeric datasets
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
Std Dev in [min, max] | ✅ |
| Std Dev < min or > max | ❌ |
Column Values To Be At Expected Location
Validates latitude/longitude values are within a defined area.
Dimension
Accuracy
When to Use
- Verifying address coordinates
- Mapping regional data
Behavior
| Condition | Status |
|---|---|
| Coordinates within buffer of expected location | ✅ |
| Any record outside allowed radius | ❌ |